Hp ProLiant ML370 G6 Server User Manual Page 47
- Page / 172
- Table of contents
- TROUBLESHOOTING
- BOOKMARKS
Rated. / 5. Based on customer reviews


Hardware options installation 47
Memory subsystem architecture
The memory subsystem in this server is divided into channels. Each processor supports three channels, and
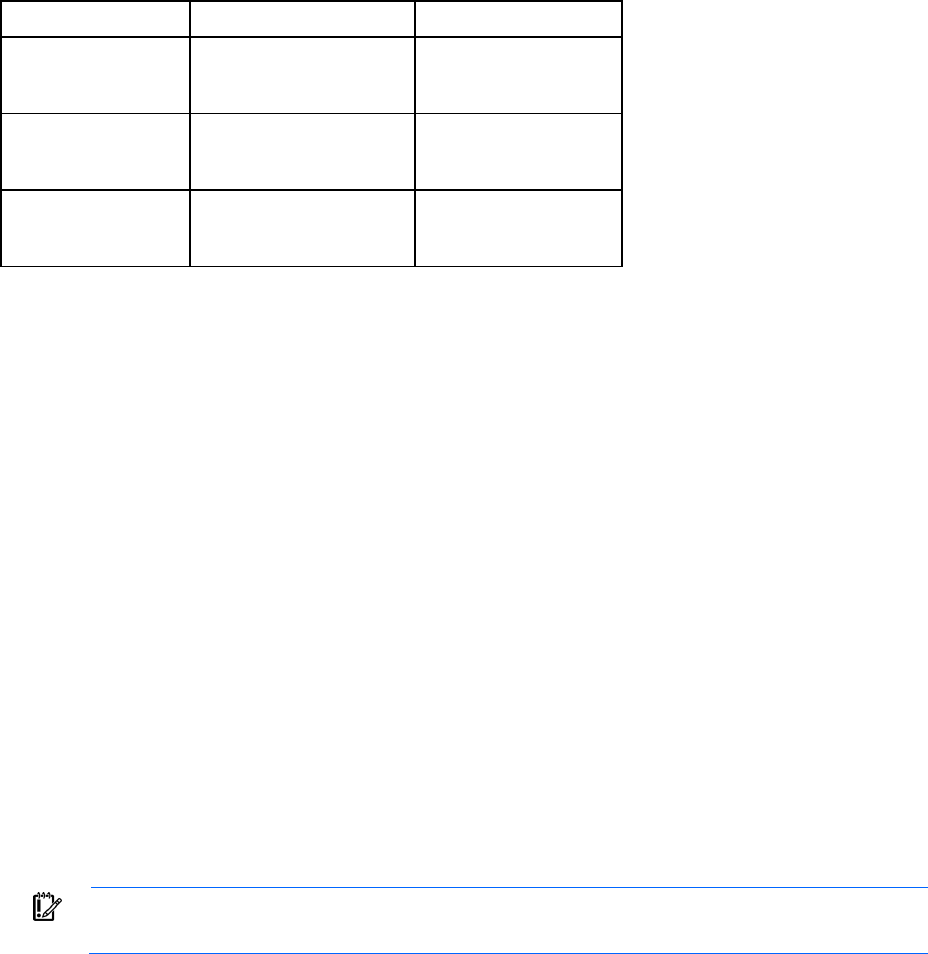
each channel supports three DIMM slots, as shown in the following table.
Channel Population order Slot number
1
G
D
A
1
2
3
2
H
E
B
4
5
6
3
I
F
C
7
8
9
This multi-channel architecture provides enhanced performance in Advanced ECC mode. This architecture
also enables the Lockstep, Online Spare, and Mirrored Memory modes. This server supports both Registered
PC3 DIMMs (RDIMMs) and Unbuffered DIMMs (UDIMMs).
DIMM slots in this server are identified by number and by letter. Letters identify the slots to populate for
specific AMP modes. Slot numbers are reported by ROM messages during boot and for error reporting.
Single-, dual-, and quad-rank DIMMs
To understand and configure memory protection modes properly, an understanding of single-, dual-, and
quad-rank DIMMs is helpful. Some DIMM configuration requirements are based on these classifications.
A single-rank DIMM has one set of memory chips that is accessed while writing to or reading from the
memory. A dual-rank DIMM is similar to having two single-rank DIMMs on the same module, with only one
rank accessible at a time. A quad-rank DIMM is, effectively, two dual-rank DIMMs on the same module. Only
one rank is accessible at a time. The server memory control subsystem selects the proper rank within the
DIMM when writing to or reading from the DIMM.
Dual- and quad-rank DIMMs provide the greatest capacity with the existing memory technology. For
example, if current DRAM technology supports 2-GB single-rank DIMMs, a dual-rank DIMM would be 4-GB,
and a quad-rank DIMM would be 8-GB.
DIMM identification
IMPORTANT: This server does not support mixing RDIMMs and UDIMMs. Attempting to mix
these two types causes the server to halt during BIOS initialization.
- User Guide 1
- Contents 3
- Contents 4 4
- Contents 5 5
- Contents 6 6
- Component identification 7
- Front panel LEDs and buttons 8
- Systems Insight Display LEDs 9
- Rear panel components 11
- Rear panel LEDs 12
- System board components 13
- DIMM slots 14
- System maintenance switch 14
- NMI functionality 15
- SAS and SATA device numbers 16
- SAS and SATA hard drive LEDs 17
- Battery pack LEDs 19
- FBWC module LEDs 20
- Operations 22
- Operations 23 23
- Operations 24 24
- Remove the access panel 25
- Remove fans 1-4 26
- Remove fan 5 26
- Remove the air baffle 28
- Remove the fan cage 29
- Remove the media bay blank 30
- Remove the DVD-ROM drive 31
- Operations 32 32
- Rack planning resources 33
- Optimum environment 34
- Power requirements 35
- Temperature requirements 35
- Rack warnings 36
- Server warnings and cautions 36
- Setup 37 37
- Installing hardware options 38
- Setting up a tower server 38
- Setup 39 39
- Registering the server 40
- Introduction 41
- Processor option 41
- Memory options 46
- DIMM identification 47
- Memory configurations 48
- Installing a DIMM 52
- Redundant fans option 53
- Power supply configuration 55
- Save the screws 60
- Install the drive cage 63
- Six-bay LFF backplane option 64
- Connect the power cable 66
- Expansion board options 78
- Storage controller option 84
- BBWC and FBWC options 84
- Installing the cache module 85
- HP SAS Expander Card option 87
- Graphics adapter option 88
- Rear (1) 92
- Front (2) 92
- Install the I/O bezel 97
- Cabling 103
- SAS hard drive cabling 104
- Item Description 105
- • Drive cage bay 1 106
- • Drive cage bay 2 106
- SAS expander cabling 108
- Media device data cabling 109
- DVD-ROM drive cabling 110
- Power cabling 111
- Front panel cabling 114
- Cabling 115 115
- Configuration tools 116
- Using RBSU 117
- Auto-configuration process 117
- Boot options 118
- BIOS Serial Console 118
- Configuring AMP modes 118
- Configuring mirrored memory 118
- Array Configuration Utility 119
- Management tools 121
- Erase Utility 122
- Redundant ROM support 122
- Diagnostic tools 123
- Integrated Management Log 124
- Keeping the system current 125
- Firmware 126
- HP Smart Update Manager 126
- Care Pack 127
- Troubleshooting 128
- Symbols on equipment 129
- Warnings and cautions 129
- Symptom information 130
- Loose connections 132
- Service notifications 133
- Server health LEDs 133
- Troubleshooting flowcharts 133
- General diagnosis flowchart 134
- Symptoms: 136
- Troubleshooting 138 138
- POST problems flowchart 139
- OS boot problems flowchart 141
- Troubleshooting 142 142
- • Redundancy failure 143
- (http://www.hp.com/support) 144
- Troubleshooting 145 145
- Battery replacement 146
- Battery replacement 147 147
- FCC rating label 148
- Class A equipment 148
- Class B equipment 148
- Modifications 149
- • EMC Directive 2004/108/EC 150
- Japanese notice 151
- BSMI notice 151
- Korean notice 151
- Chinese notice 152
- Laser compliance 152
- Battery replacement notice 152
- Electrostatic discharge 154
- Specifications 155
- Technical support 158
- Technical support 159 159
- Customer Self Repair 160
- Technical support 161 161
- Reparo feito pelo cliente 162
- Technical support 163 163
- Technical support 164 164
- Technical support 165 165
- Acronyms and abbreviations 166
- Index 169 169
- Index 170 170
- Index 171 171
- Index 172 172
 (98 pages)
(98 pages)







Comments to this Manuals